7 Common Reasons to Go to Physical Therapy
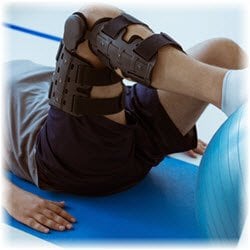 Physical therapy provides so many benefits that you may not realize all the reasons it’s worth a try.
Physical therapy provides so many benefits that you may not realize all the reasons it’s worth a try.
Physical therapy is a proven treatment method that helps people heal from injuries, disabilities and health conditions. Some of its many benefits include pain management, improved mobility and muscle strengthening.
Each person’s needs and goals for physical therapy are unique. After a therapist does an evaluation of your condition and reviews your medical history, together you will establish short and long term goals. The therapist will then create a routine to help you meet those goals. Exercise is a main component of physical therapy, but recommended treatments may also include posture correction and alignment, balance and coordination training, and stress-relieving routines.
Here are 7 common reasons to seek physical therapy treatment:
- Pain management: Therapeutic exercises and manual therapy techniques can help relieve pain and restore muscle and joint function. Physical therapy can help reduce or eliminate the use of opioids for pain relief.
- Mobility improvement: Stretching and strengthening exercises help restore your ability to move better at any age. Whether you have a chronic condition like arthritis, are recovering from an injury or are managing age-related mobility issues, physical therapy may help.
- Surgery avoidance: If physical therapy helps you manage pain or heal from an injury, surgery may not be needed. If you do need surgery, pre-surgery therapy can help you go into surgery in better shape, which can help speed recovery.
- Sports injury recovery: Physical therapists can design recovery or prevention exercise programs to ensure a safe return to a sport. Some injuries that can be treated during physical therapy include tennis elbow, groin pulls, shin splints, hamstring strains, shoulder injuries, sprained ankles, knee injuries and Achilles tendinitis.
- Stroke recovery: Physical therapy helps strengthen weakened parts of the body and improve posture and balance after having a stroke. Therapists can also improve stroke patients’ ability to be more independent by helping them return to performing everyday tasks.
- Fall prevention: Physical therapy can improve coordination and balance, which reduces the likelihood of falls. Therapists can also recommend assistive devices and provide training on the proper way to use these devices to improve safety and reduce fall risk.
- Health condition management: In addition to treating ailments such as arthritis and sports injuries, some physical therapists offer specialized management of health conditions, such as bowel or urinary incontinence, breast cancer, fibromyalgia and lymphedema, among others.
Regardless of your reason for starting physical therapy, being patient and persistent is the best way to see lasting results and continued improvement.
Copyright 2021 © Baldwin Publishing, Inc. All rights reserved. Health eCooking® is a registered trademark of Baldwin Publishing, Inc. Cook eKitchen™ is a designated trademark of Baldwin Publishing, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein without the express approval of Baldwin Publishing, Inc. is strictly prohibited.